Abstract
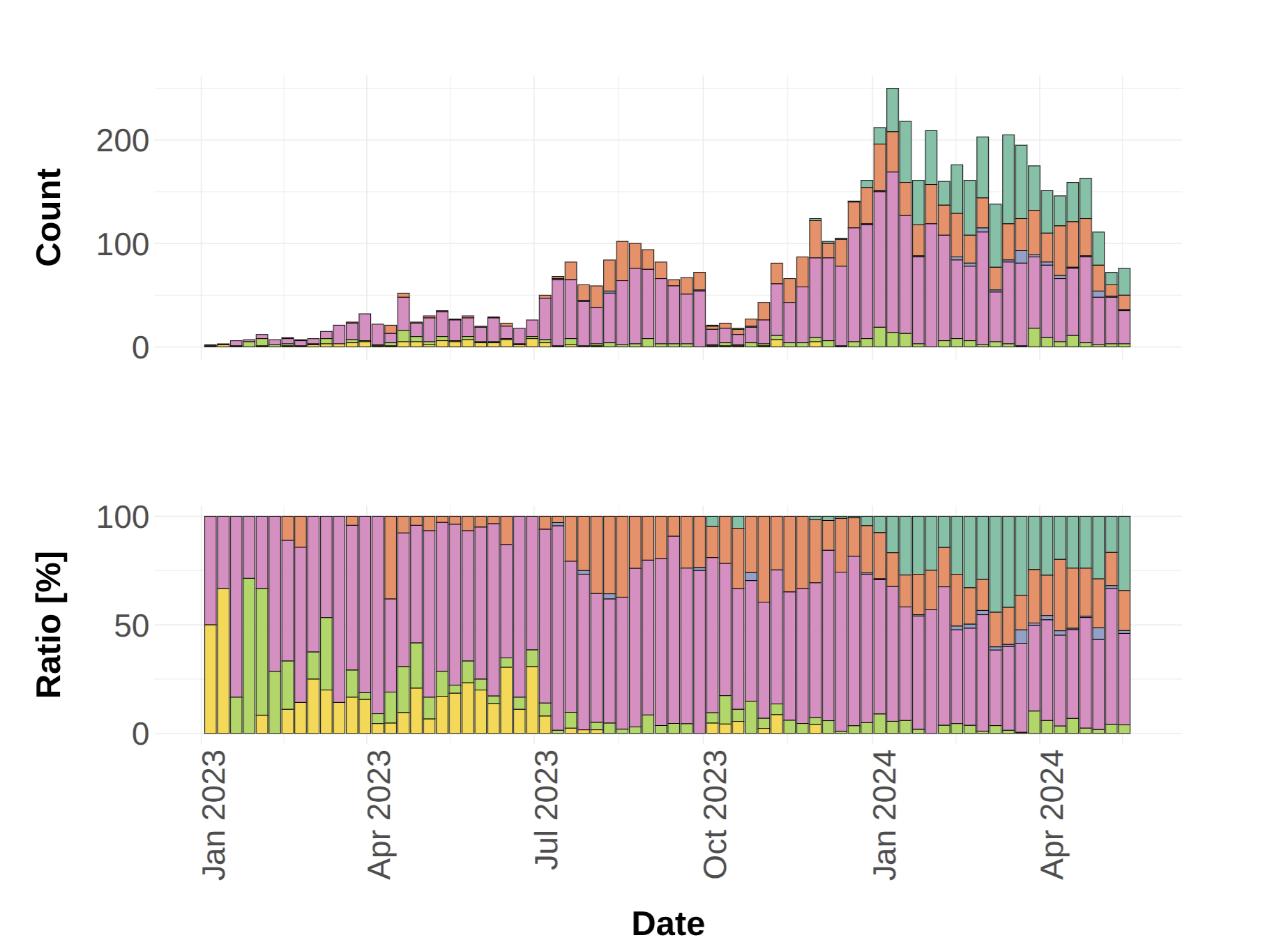
Large language models (LLMs) have become central to both academic research and industrial applications, fueling debates on their accuracy, usability, privacy, and potential misuse. While proprietary models benefit from substantial investments in data and computing resources, open-sourcing is often suggested as a means to enhance trust and transparency. Yet, open-sourcing comes with its own challenges, such as risks of illicit applications, limited financial incentives, and intellectual property concerns. Positioned between these extremes are hybrid approaches—including partially open models and licensing restrictions—that aim to balance openness with control. In this paper, we adopt a data-driven approach to examine the open-source development of LLMs. By analyzing contributions in model improvements, modifications, and methodologies, we assess how community efforts impact model performance. Our findings indicate that the open-source community can significantly enhance models, demonstrating that community-driven modifications can yield efficiency gains without compromising performance. Moreover, our analysis reveals distinct trends in community growth and highlights which architectures benefit disproportionately from open-source engagement. These insights provide an empirical foundation to inform balanced discussions among industry experts and policymakers on the future direction of AI development.
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/15/5/2790